Direct and Indirect Speech is used to express the content of any statements, questions or other utterances made by anyone. There are to ways to express the statement, question or utterance. One is Direct Speech and Second one is Indirect Speech. In Direct Speech, we quote the statement as it was made. But in indirect speech, we have a slight change in words of the one who is making the statement. We don’t quote the exact words.
Direct and Indirect Narration
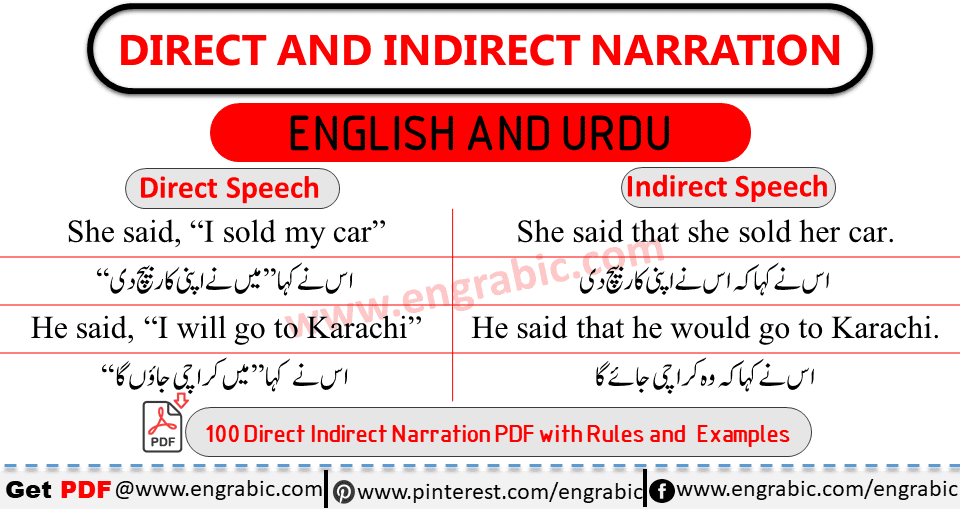
Direct Speech: When we report the exact words of speaker, without any change then this mood of communication is called direct speech.
Example: He said, “I am hungry”
Here the exact words of speaker are I am hungry and those are repeated without any change.
Indirect Speech: When we do not report the real words of speaker and change them, this mood of communication is called indirect speech.
Example: He sad that he was hungry.
Here we changed the real words of speaker. I am hungry to He was hungry.

You May Download This Lesson in PDF Form at the Bottom of Page

| Parts of Direct Speech | |
| Reporting Speech | Reported Speech |
| It contains the words of speaker, the person who is reporting the message | Contains words of speaker whose message is reported |
| He said, “I will call you | |
| He said = Reporting Speech | I will call you = Reported Speech |


Changes of Tenses:
| Tenses | Changes to |
| Present indefinite | Past Indefinite |
| Present Continuous | Past Continuous |
| Present Perfect | Past Perfect |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Past indefinite | Past Perfect |
| Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Past Perfect | Past Perfect |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Past perfect continuous |
| In all future tenses “will” | Changes into “Would” |
You May Download This Lesson in PDF Form at the Bottom of Page
Important Words to Change
| Direct | Indirect |
| Today | That day |
| Yesterday | The day before |
| Tomorrow | Following day |
| Is, am | Was |
| Was, were | Had been |
| Did | Had |
| Will, shall | Would |
| Can | Could |
| Must | Had to |
| Ago | Before |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Last | The previous |
| Are | Where |
| May | Might |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| It | That |
| next | The following |
Change in Pronoun:
1 st Person Pronouns
All the first person pronouns (I, my, mine, myself, we, our, us, ours, ourselves) are changed according to the subject reporting speech.
Example:
She said, “I sold my car myself”
She said that she sold her car herself.
You May Download This Lesson in PDF Form at the Bottom of Page
2 nd Person Pronouns
All the second person pronouns (you, your, yours, yourself) are changed according to the subject of reporting speech.
Example:
She said to me, “You wasted your precious time yourself”
She told me that I wasted my time myself
3 rd Person Pronouns
Al the third person pronouns will remain unchanged.
He said, “She is busy with her toys”
She said that she was busy with her toys.
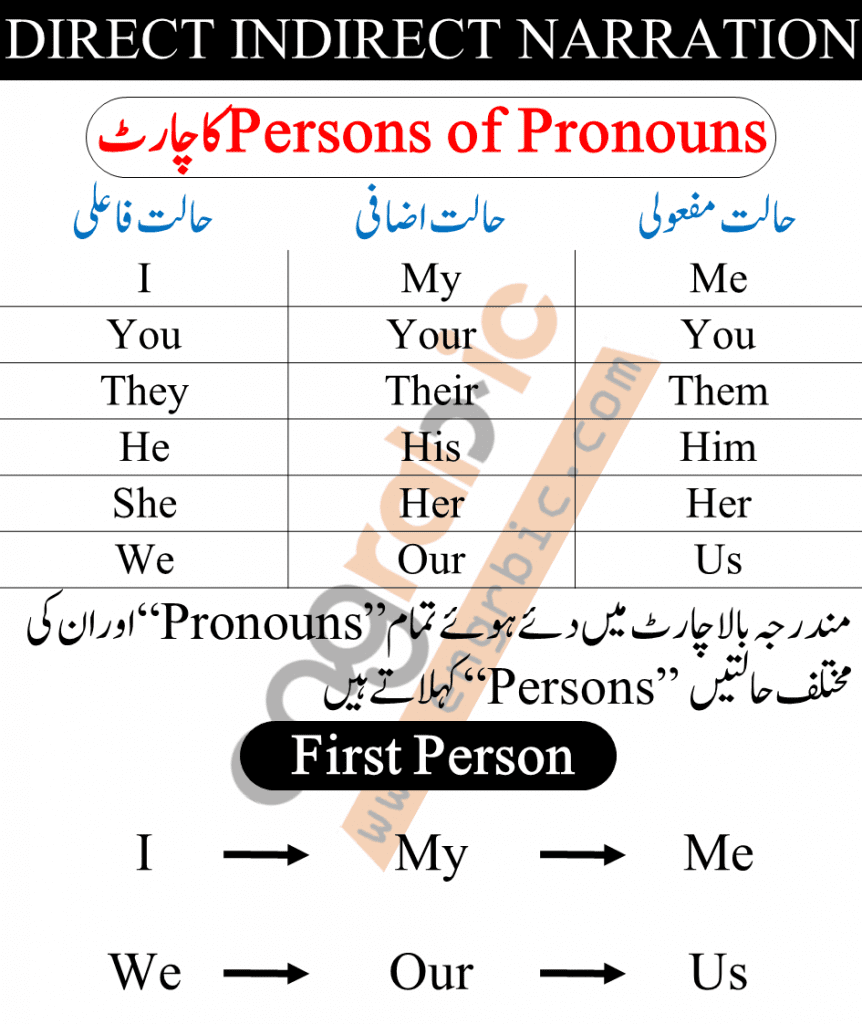
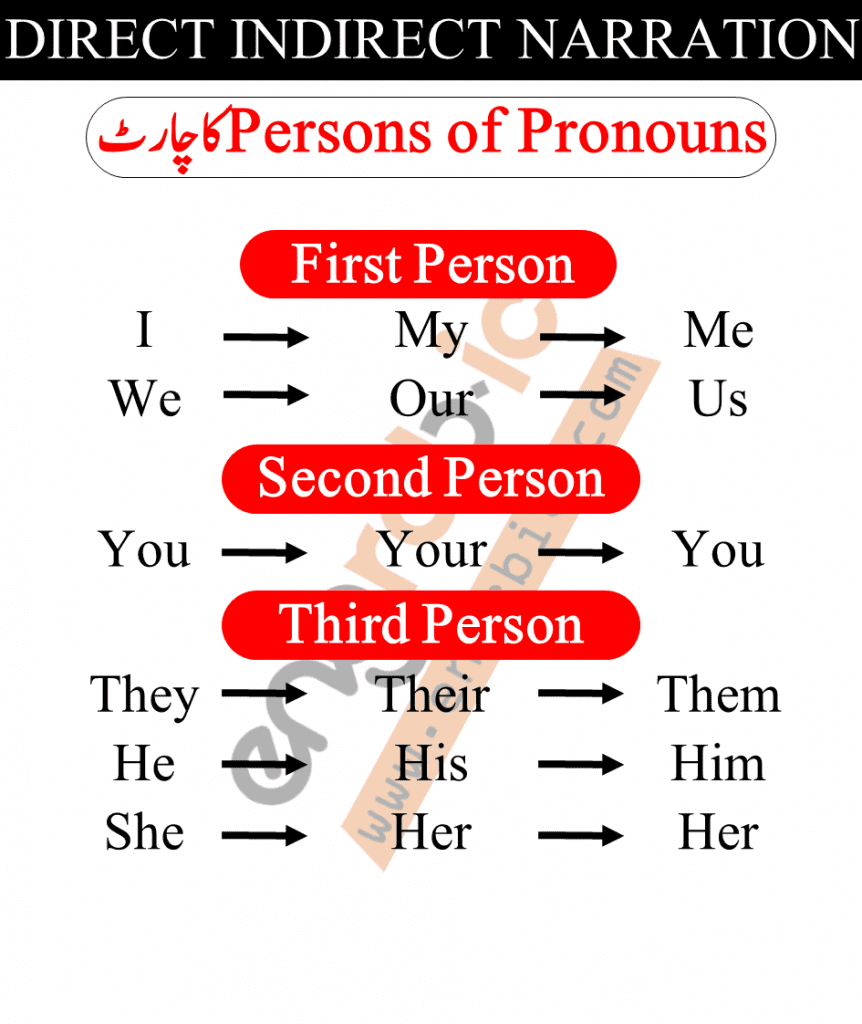
Persons of Pronouns
| I | My | Me |
| You | Your | You |
| They | Their | Them |
| He | His | Him |
| She | Her | Her |
| We | Our | Us |
First Person
| I | My | Me |
| We | Our | Us |
Second Person
| You | Your | You |
Third Person
| They | Their | Them |
| He | His | Him |
| She | Her | Her |
You May Download This Lesson in PDF Form at the Bottom of Page
How to change interrogative sentences
The word said is usually changed into asked or inquired. Full stop or period replaces sign of interrogative or question mark.
Example:
She said, “Do you know me?”
She asked if I knew her.
How to change imperative sentences
Example:
She said, “Get out of my way”
She told me to get out of her way.
She said to me, “Please come with me”
She requested me to come with her.
How to change appetitive sentences
Sentences which show wish, desire, hope and prayer.
The word said changes into prayed and may changes into might.
Example:
My mother said to me, “May you live long”
My mother prayed that I might live long.
You May Download This Lesson in PDF Form at the Bottom of Page
How to change exclamatory sentences
Sentences which express joy, exclamation, sorrow, admiration, surprise or other such feelings. Interjection such as Ah! Oh! Alas! Hurrah!
The word said changes into exclaimed with, after which expressed feelings such as joy, sorrow, surprise, delight, happy, admiration, disgust and horror are used.
Example:
He said, “What a lovely sight!”
He exclaimed with admiration that it was a lovely sight.
Get FREE PDF HERE